

Stimulation of the autonomic nervous system's sympathetic branch, known for triggering "fight or flight" responses when the body is under stress, induces pupil dilation.
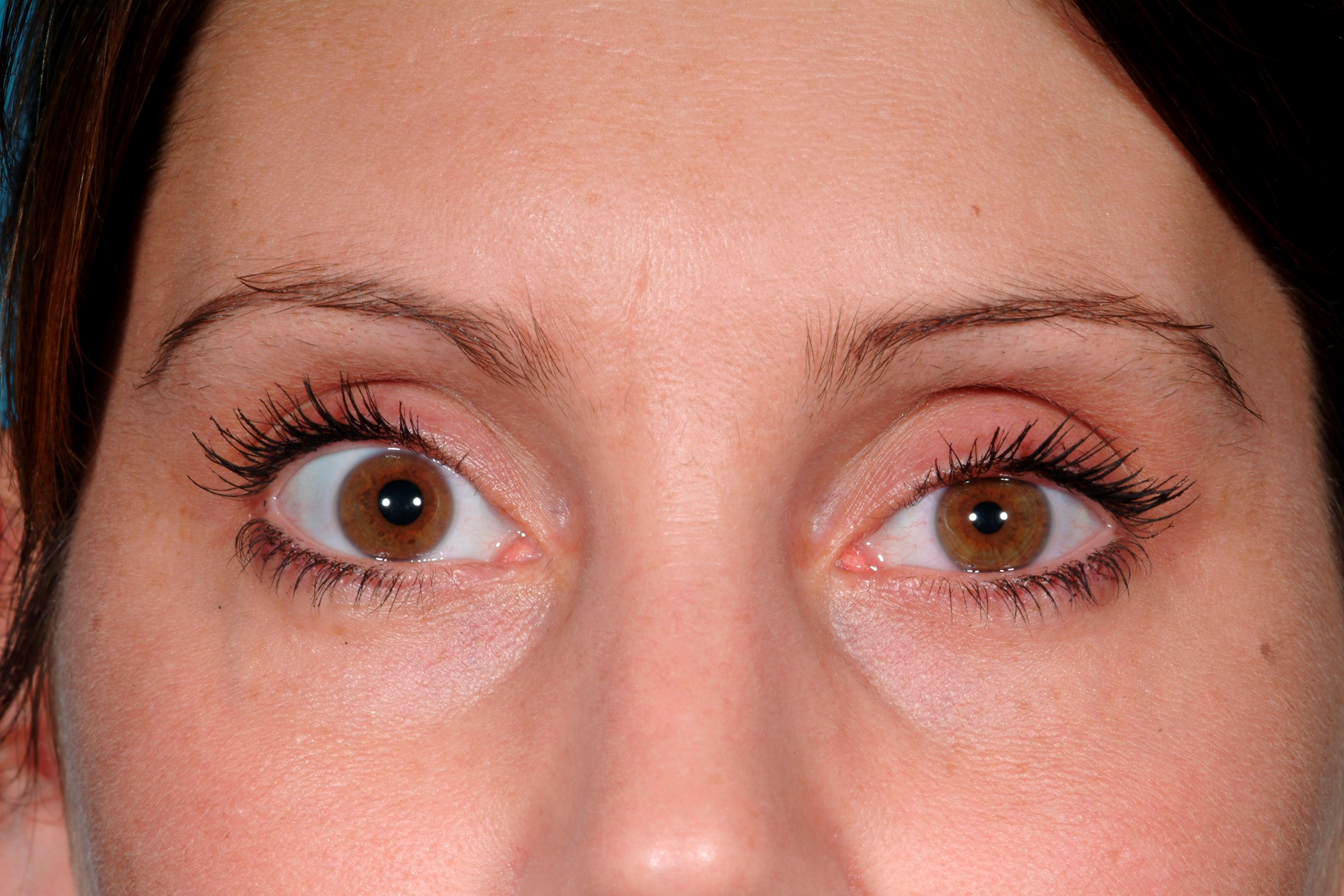
The iris is made of two types of muscle: a ring of sphincter muscles that encircle and constrict the pupil down to a couple of millimeters across to prevent too much light from entering and a set of dilator muscles laid out like bicycle spokes that can expand the pupil up to eight millimeters-approximately the diameter of a chickpea-in low light. Specifically, it dictates the movement of the iris to regulate the amount of light that enters the eye, similar to a camera aperture. But a different, older part of the nervous system-the autonomic-manages the continuous tuning of pupil size (along with other involuntary functions such as heart rate and perspiration). The visual cortex in the back of the brain assembles the actual images we see. He views the dilations as a by-product of the nervous system processing important information. "Nobody really knows for sure what these changes do," says Stuart Steinhauer, director of the Biometrics Research Lab at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. And they do this without knowing exactly why our eyes behave this way.

In fact, pupil dilation correlates with arousal so consistently that researchers use pupil size, or pupillometry, to investigate a wide range of psychological phenomena. They also betray mental and emotional commotion. What do an orgasm, a multiplication problem and a photo of a dead body have in common? Each induces a slight, irrepressible expansion of the pupils in our eyes.įor more than a century scientists have known that our eyes' pupils respond to more than changes in light.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
